Organic Drumstick Production for Better Livelihoods of Marginal Farmers
1. Introduction
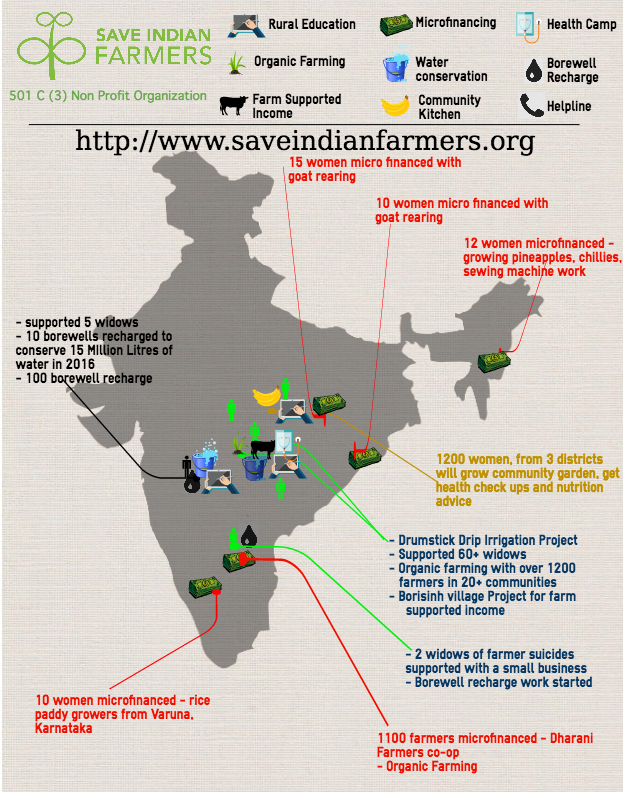
Save Indian Farmers (SIF) is a United States based nonprofit organization working for Indian agrarian community. Save Indian Farmers (SIF) is supporting drumstick cultivation for marginal farmers through partner organization in Marathwada region (Beed and Parbhani Districts) of Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh. Through drumstick cultivation SIF is supporting marginal farmers to have better income and his family`s nutritional security as drumstick have good nutritional value.
2. Why Drumsticks?
- Requires less water
- All types soil are suitable
- Perennial crop
- Resistance to most of pests and diseases
3. Objectives of Drumstick Production Initiative
- To increase the income of marginal farmers
- Nutritional security to family members of marginal farmers
- To contribute for better livelihoods of marginal farmers
4. Area of Support to Marginal Farmers
- To provide healthy and high yielding planting material (variety)
- To contribute in providing micro-irrigation (Drip) facility
- To provide guidance to farmers for higher quality organic production of drumstick
- To provide support for drumstick marketing
5. Scientific Name of Drumstick: Moringa oleifera
6. Nutritional Value and Health Benefits of Drumstick (source: https://www.healthbenefitstimes.com/drumsticks/)
Calories: 42 Kcal./cup
Major nutrients in drumstick:
- Vitamin C (127.22%)
- Vitamin B5 (16.54%)
- Total dietary Fiber (13.16%)
- Manganese (12.35%)
- Magnesium (11.90%)


Health Benefits:
Improves Nervous and Immune system, Fights cold and flu, For strong bones, Pregnancy and Lactation, Avoids infection, Digestive Disorders, Lung problems, Excellent iron tonic, Glowing skin, Tonic for Children, Urinary Disorders, Increases Bone Density, Reduces Cancer Level, Reduces Intestine Tumor or Ulcer, Improves Vision of Eye and Retina, Asthma, Bronchitis, Tuberculosis, Beneficial for Brain Injury, Improves Digestion problem, Reduces Diabetic Level, Makes Gall Bladder Healthy, High acidic Urine (Dysuria).
7. Drumstick Package of Practices (POP) from planting to harvesting and post harvesting
1. Climatic condition for drumstick cultivation
Hot and humid climate is suitable for growth and dry climate for flowering. The temperature of 25 to 30 degree Celcius is suitable for flowering in drumstick.
2. Soil Requirement for drumstick cultivation
Drumstick grows best in a well drained loam to clay loam. Soil pH should be 6.2 to 7. It cannot withstand prolonged water logging.
3. Land preparation
Two times ploughing should be done. Pits are prepared
4. Planting period
June-July or January month
5. Good Drumstick varieties
Local varieties: Rohit 1, PKM 1, PKM 2, Coimbatore 1, Dhanraj
6. Planting method
It is advised to transplant one month old plant
7. Planting distance/Spacing
The spacing between two plants is maintained at 3 x 3 meter.
8. Water Management
Water requirement is less for this plant; hence this is capable of giving yield in drought condition also but to a lesser extent. But with following proper irrigation methods like drip irrigation and fertigation, it will give more yield.
9. Irrigation method
Good yield by using drip irrigation method
10. Weed Management
Weeding of unwanted growth of plants to be done regularly. Intercropping with other vegetations can control weeds.
11. Manuares and Fertilizers
Farm Yard Manuare (FYM) 20 tonnes per hectare. Each pit applied with 8-10 kg FYM.
12. Pest Management
Leaf eating caterpillar and Hairy caterpillar occurring in the rainy season destroys the leaves. Pheromone traps were used to manage the pest.
Jassides and Mites: This pest sucks the sap and releases honey like substance. Sticky traps were installed in field to manage this pest.
Bark eating caterpillar: This can be controlled by mechanical method by adding iron rod or tar or addition of cotton ball soaked in petrol in the hold. The spraying may be done in the morning or evening hours.
13. Disease Management
Rotting of stem in water logging condition. Drain excess water from the field.
14. Pruning
When the plant reaches one metre, the apex shoot of the plant may be removed to allow lateral shoots to emerge for better productivity and yield. Proper support may be given to each plant. First pruning should be done after 2 months of planting or when the plant reaches a height of one metre.
15. Harvesting
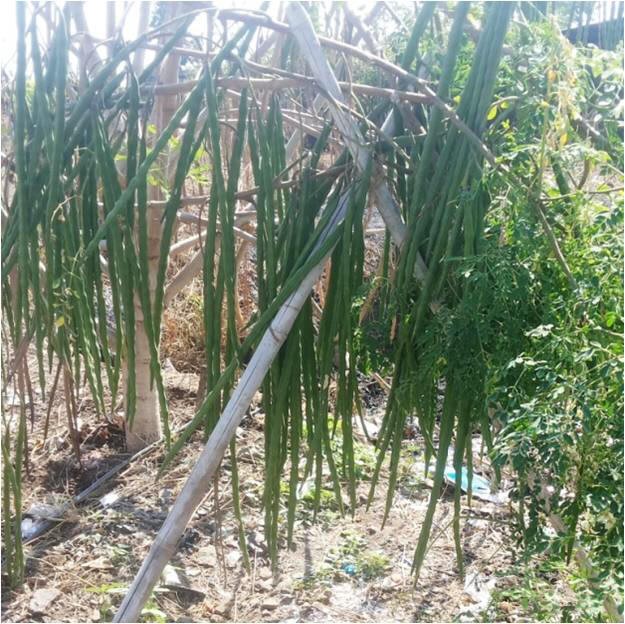

16. Yield:
50-55 tonnes of pods per hectare or 220 pods per tree
17. Export Potential
African countries, North America, Middle East, European countries, Russian and Australia besides huge Indian home market.
18. Post Havesting Technology
While pods and green leaves have to be sold soon they are harvested for consumption as food, the leaves and seeds can be preserved for future consumption. Leaves can be dried in shade, powdered and kept stored properly for use in food preparations, as the high nutritive value of the leaves makes it a preferable source of nutrition. The seeds are useful for oil extraction which is used in soap making, in medicinal preparations and as lubricant in fine machines like watches. The seed is also used in powdered form for medicinal use. They can be stored more than one year for further use of propagation or consumption.
19. Value Added Products
- Drumstick leaf powder in packages and container
- Drumstick pickles
- Drumstick oil – due to low viscosity it is used in precision industry as lubricant especially in Western European countries
- Drumstick pods cake
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
About the Author:
Yashwantrao Yadav is a Doctoral scholar at Tata Institute of Social Sciences (TISS), Mumbai and also a member of Save Indian Farmers and involves in field activities